Ginsenoside
Ginsenoside
The Active Components in Ginseng: Ginsenosides
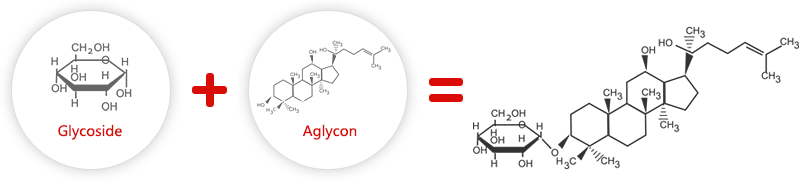
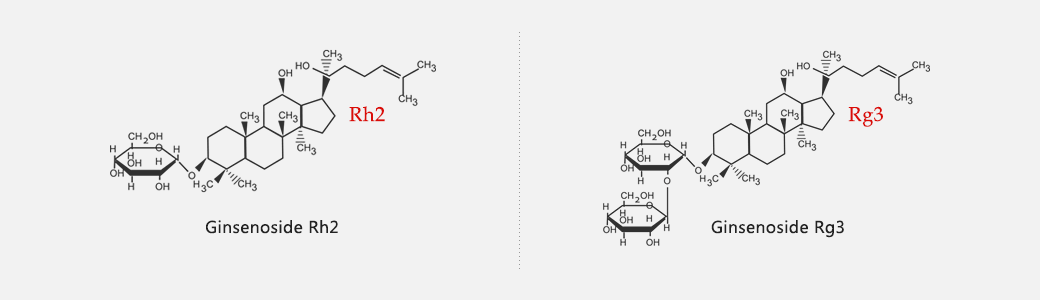
Ginsenosides (also known as ginseng saponins) are the chief active components in ginseng. Because it has been found that many ginsenosides have special biochemical properties, these compounds have attracted growing scientific interest in recent years, and more than 60 different ginsenoside structures have been discovered thus far. Ginsenosides belong to a family of sterol compounds. Saponins refer to natural glycoside compounds containing one or more glycoside moieties and a aglycone. Because compounds of this type tend to make foam when mixed with water, they are referred to as saponins. Commonly seen ginsenosides including Rb1, Rb2, Rb3, Rc, Rd, Rg3, Rh2, glycosyl PPD and the panaxadiol Rh2 and Rg3, which have only been discovered in plants in the genus Panax. Each kind of ginsenoside has its own unique functions. Because ginsenosides are present in only small amounts in natural ginseng, difficult to extract, and the cost of purification and conversion is high, the prices of ginsenosides are steep. In particular, the ginsenosides Rh2, Rg3 and rare ginsenosides are especially valuable. They are only found in levels of 0.001% and 0.03% in red ginseng. However, rare ginsenosides which are the metabolic products of the bacterial flora in the human gut do not exist in any ginseng. Their value is extremely precious.
Ginsenoside in Wikipedia │ Ginsenoside Manufacturing and R&D Center
Internationally Patented Technology; Excellent Extraction Quality
- International patents: The world's first use of bioconversion methods in the commercial mass production of rare ginsenosides.
- Special technology: Use of the low-acid degradation method in the commercial mass production of high-priced rare ginsenosides.
- Integration of many key technologies, superior leadership, assured quality.
- From Taiwan's only and the world's leading ginsenoside raw material manufacturing and R&D center.
- Taiwan's sole specialized R&D firm able to perform bioactivity and toxicological screening of ginsenosides in cells and animals.
The ginsenoside content of ginseng will differ depending on the part of the plant, processing method, age of the plant when harvested, and the geographical location where it was grown. The ginsenoside content of the taproot of white ginseng is about 2.0~3.5%; of the taproot of red ginseng about 3.8~4.9%; of adventitious roots 4.9%; of rhizomes 6.4%; of terrestrial stems 2.1%; of ginseng side roots 6.5~12.0%; of white ginseng tail 9.3~12.3%; of red ginseng tail 8.3~11.7%; of flower buds 15.0%; of pulp 8.9%; of seeds 0.7%; of ginseng skin 8.0~8.8%, and of ginseng leaves 7.6~12.6%.

 Facebook
Facebook